Explanation of CPU & GPU
14 July, 2020
This article discusses about the different CPU & GPU architectures, their evolve & generations.
Also big fish companies who manufactures these products.
But these article is limited to only x-86 based processors.
CPU = Central Processing Unit
GPU = Graphics Processing Unit
Two of the major company who manufactures cpu & gpu for consumer desktop & laptop’s are
INTEL(US) & AMD(Advanced Micro Devices)(US)
Intel Processors Link to heading
Processor names often don’t say the architecture, generations. So buying a cpu can be confusing.
Intel cpu name examples are :
- Pentium 1, 2, 3, 4
- Celeron
- Pentium M and Celeron M for mobile devices
- Pentium Dual Core
- Core Solo
- Core Duo
- Core 2 Duo
- Core 2 Quad
- Core i3, i5, i7, i9
Here’s a sample intel processor name
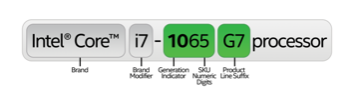
Brand
The Intel naming scheme starts with the processor’s brand—the overall product line the processor was created for.
Today, the most common Intel® processor names begin with Intel® Core™, Intel® Pentium®, and Intel® Celeron®.
Intel® Pentium® and Intel® Celeron® processors are economical product lines created for price-conscious consumers.
Intel® Core™ processors bring faster performance and additional features not available in Intel® Pentium® and
Intel® Celeron® models. Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors offer a higher level of performance for servers
and workstations
Brand Modifier
Intel® Core™ series processors include a brand modifier before the remaining parts of the model number. Intel® Pentium®
and Intel® Celeron® processors do not use this naming convention. Today, the Intel® Core™ series includes the brand
modifiers i3, i5, i7, and i9. Higher brand modifier numbers offer a higher level of performance and, in some cases,
additional features (like Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology). For example, within a given processor family,
an i7 will outperform an i5, which will outperform an i3.
Generation Indicator
After the brand and brand modifier comes the processor’s generation indicator. Intel® processor generations are
identified in the processor number in all Intel® Core™ processor brands. In a four-digit processor number,
the first digit typically represents the generation. For example, a processor with the digits 9800 is a 9th Gen
processor, while one labeled 8800 is 8th gen technology.
For 10th Generation Intel® Core™ processors, the Intel naming scheme differs slightly (see below).
However, the first two digits in the product number will be 10.
SKU Numeric Digits
For the majority of Intel® processors, the final three digits of the product number are the SKU. SKUs are generally
assigned in the order in which processors in that generation and product line are developed. A higher SKU within
otherwise-identical processor brands and generations will generally have more features. However, SKU numbers are not
recommended for comparison across different generations or product lines.
Product Line Suffix
The SKU suffix is another key indicator of the processor’s capabilities. These remaining differences are indicated
by a letter-based product line suffix. For example, within the Intel® Core™ series, U indicates a processor that has
been designed for power-efficient laptops or 2-in-1s. Meanwhile, XE indicates an “extreme edition” processor for
desktops designed for maximum performance.
| Suffix | Meaning |
|---|---|
| F | Requires discrete graphics |
| G | Includes discrete graphics on package |
| H | High performance optimized for mobile |
| HK | High performance optimized for mobile, unlocked |
| HQ | High performance optimized for mobile, quad core |
| K | Unlocked |
| S | Special edition |
| T | Power-optimized lifestyle |
| U | Mobile power efficient |
| Y | Mobile extremely low power |
X SERIES PROCESSORS
X/XE – Extreme performance and mega-tasking, unlocked
Intel CPU brands Link to heading
Pentium Gold, Silver & J series processors. Very low power. Intel® Pentium® processor—from sleek laptops, 2 in 1s, and mini PCs, to stylish desktop PCs with great battery life, and performance for common applications
Intel Celeron Entry level PCs and portable devices that fit your lifestyle and budget
ATOM P, C, x7 x5, x3, E series Mobile devices that start faster, work longer, and support high-res Ultra HD 4K multimedia and high Frames Per Second (FPS) streaming.
Intel Atom® P processors introduce a new class of high throughput, low latency processing for high-density network edge and security solutions
Intel® Xeon® Processors XEON cloud computing, real-time analytics, processing for your mission-critical business, and big data insights
10th Gen Intel® Core™ U-Series Processor
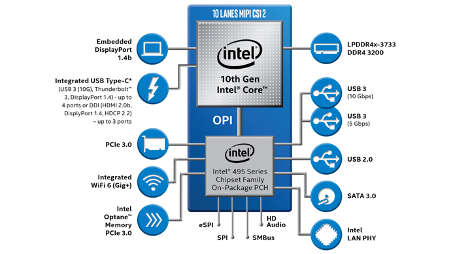
10th Gen Intel® Core™ Y-Series Processor
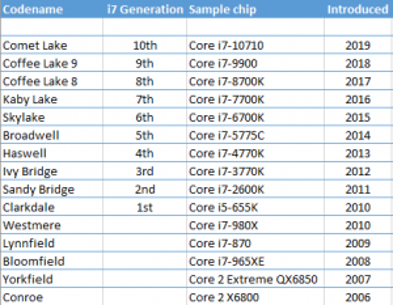
Intel CPU Generations Link to heading
- 1st Generation Intel Processors – Nehalem
- 2nd Generation Intel Processors – Sandy Bridge
- 3rd Generation Intel Processors – Ivy Bridge
- 4th Generation Intel Processors – Haswell
- 5th Generation Intel Processors – Broadwell
- 6th Generation Intel Processors – Skylake
- 7th Generation Intel Processors – Kaby Lake
- 8th Generation Intel Processors – Kaby Lake R / Coffee Lake 8
- 9th Generation Intel Processors – Coffee Lake 9
- 10th Generation Intel Processors –
Comet Lake/ Cannon Lake / Ice Lake - 11th Generation Intel Processors – Tiger Lake
7th Generation Intel Processors – Kaby Lake
Intel’s 7th generation processors, codenamed Kaby Lake, were introduced in 2016. Kaby Lake is essentially a refresh of
Sky Lake architecture with few efficiencies and power improvements. It uses a 14-nm process architecture.
Kaby Lake is the first micro-architecture from Intel that does not come with an official driver for Operating Systems
older than Windows 10.
Kaby Lake introduced a new graphics architecture to improve 3D graphics performance and 4K video playback.
It uses 1151 LGA sockets and has dual-channel support for DDR3L-1600 and DDR4-2400 RAM slots.
8th Generation Intel Processors – Kaby Lake R
In 2017, Intel introduced a refresh of Kaby Lake processors as their new 8th generation release. The details are the
same as mentioned in the 7th Generation Intel Processor but some 8th generation chipsets have support for DDR4-2666
RAM but lack DDR3L RAM support.
9th Generation Intel Processors – Coffee Lake
Coffee Lake processors were introduced by Intel in late 2017. With this architecture, Intel Core i9 processors were
introduced.
Coffee Lake processors break the limit of 4 cores per CPU. The new processors can now support up to 8 cores per CPU.
Since the heat produced in these cores will be enormous, Intel attached the integrated heat spreader (IHS) to the CPU
die instead of the thermal paste which is normally used in earlier processors.
It uses 1151 LGA sockets with altered pinouts to support more than 4 cores along with up to 16 MB of L3 cache.
10th Generation Intel Processors – Cannon Lake/Ice Lake
Cannon Lake, Intel’s 10th generation architecture, comes with an all-new 10-nm technology. It was released in late 2017
but production properly started in 2018.
Ice Lake is produced as the 2nd generation of 10-nm processors.
They use BGA1526 sockets and come with DDR4 3200 and LPDDR4X 3733 support. This is the first CPU architecture that
comes with integrated support for Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) and Thunderbolt 3.
11th Generation Intel Processors – Tiger Lake
The 11th generation Intel, Tiger Lake, is yet to be released. They will be the third generation of 10-nm transistor
technology. According to Wikipedia, Tiger Lake architecture will have up to 30% performance gains as compared to
Ice Lake. L4 cache will be introduced in this generation for further performance boosts.
| Purpose | Recommended CPU |
|---|---|
| Workstation / Gaming | Intel Core i5 / i7 H Series |
| Everyday Productivity w/ a Boost | Intel Core i7 U Series / Intel Core i5 or i7 G Series |
| Super Thin (Mediocre Performance) | Intel Core m / Core i5 / i7 Y Series |
| Budget Laptops, Low Performance | Intel Celeron, Pentium |
| Super Cheap, Worst Performance | Intel Atom Series |
AMD processors Link to heading
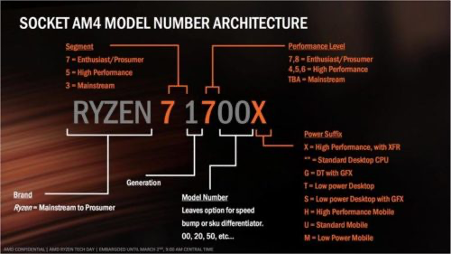
AMD Ryzen™ Desktop Processors
AMD Ryzen™ Threadripper™ Processors
- Up to 64 cores
- Up to 128 processing threads
- Up to 288MB cache
AMD Ryzen™ 9 Desktop Processors
- Up to 16 cores
- Up to 32 processing threads
- Up to 72 MB GameCache
AMD Ryzen™ 7 Desktop Processors
- 8 cores
- 16 processing threads
- Up to 36 MB GameCache
AMD Ryzen™ 5 Desktop Processors
- From 4 to 6 cores
- Up to 12 processing threads
- Up to 35MB GameCache
AMD Ryzen™ 3 Desktop Processors
- 4 cores
- Up to 8 processing threads
- Up to 18MB GameCache
AMD Ryzen Pro processors are almost identical to the normal Ryzen processors, but offer enhanced security features for enterprise use.
1000 Series - Zen Architecture, 1st Gen processors
2000 Series - Zen+ Architecture (shrunk node), 2nd Gen processors
3000 Series - Zen 2 Architecture (7nm), 3rd Gen processors
3000 or “third marketing generation” means zen2 (true second generation zen core) on desktop, but on laptops 3000 line means still zen+ (first generation zen core). 4000 line on laptops is finally zen2

Some models have Radeon Vega graphics integrated.
APU - Accelerated processing unit Link to heading
Usually processors with a discrete gpu (not graphics card) is called a APU
The “G” suffix indicates that the Ryzen processor has an AMD Radeon RX Vega graphics card. This is also true in the Intel Core I-series. Intel processors with G suffix have the AMD Radeon RX Vega graphics card.
GPU Link to heading
Mostly AMD & NVIDIA are the two of the biggest gpu producing company.
AMD bought the graphics card company ATI and incorporated as their own gpu production.
Both company mainly designs the GPU Die or underlying architectures. They license them to other companies who actually
manufactures the graphics cards. These companies are called OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturers)
ASUS, MSI, ASROCK, GIGABYTE these are the popular graphics card OEM(s).
The difference between GPU & Graphics cards is that gpu is only the processor /w die. And graphics card is the whole package with Vram, GPU fans or Cooling, RGB lighting, engraving etc. bundles as a single part with mainly PCI-e connector pins.
Nvidia manufactures some (mainly base models) graphics cards. These cards are called Founder’s Edition graphics card. AMD doesn’t make any graphics cards at all. All of AMD’s gpu’s are manufactured by OEMs. These graphics cards are called Aftermarket graphics cards.
Currently both AMD & Nvidia designs 7nm gpu dice.
AMD’s generations are:
- RDNA
- RDNA 2 / Navi 2 / Big Navi
Nvidia’s generations are :
- Pascal - 1000 series & some 1600 series
- Turing - 2000 series
- Ampere - 3000 series (upcoming)
Nvidia’s graphics cards are branded as Geforce. They have names like GTX & RTX.
GTX = Giga Texel Shader eXtreme / GeForce eXtreme RTX = Ray Tracing Shader eXtreme
Intel produces some integrated gpu’s like Intel Iris Plus which only exists in MacBooks. But they are bringing their own discrete graphics called Intel Xe graphics cards.